SEO is short for Search Engine Optimization and covers quite a bit of online search engine marketing activities to generate free traffic to a website.
Search engine optimization wasn’t rocket science, some basic web marketing techniques and a lot of hard work generating backlinks and the free Google traffic poured in and a trickle from the other search engines that didn’t provide much traffic. Website optimization isn’t as easy as it used to be.
What Search Engine Optimization Techniques Work in 2014
Search engine optimization has changed a lot over the years, much of what worked 5+ years ago is still important, we still need to use our keywords in the right locations and generate backlinks using the keywords we want ranked for as anchor text, but you can no longer rank with brute force backlinks and spammy over optimized content (it really was easy 5+ years ago). Google’s algorithms through iterations of Panda and Penguin and now Hummingbird have come a long way.
The good news is it’s not that hard to adapt your SEO copy for the Hummingbird algo and IMO it’s more fun: mindlessly repeating a main search phrase over and over again to get a good SE ranking was boring. I appreciate I’ve worked as a full-time SEO consultant for around 10 years where I sold SEO services to small and medium sized online businesses, so I’ve spent years having to create SEO optimized content and it’s not the most exciting career path :-) It’s nice to have a challenge in your work and creating Hummingbird suitable copy is far more interesting than SEM of the past.
What’s Important for Hummingbird SEO?
Google is becoming an answers engine not just a search engine.
This might seem a subtle point, Google search obviously depends on keywords, but the next time you do some long keyword searches note the “Searches related to What You Searched For” at the bottom. There’s an increasing tendency for Google to suggest question like searches like “What is SEO?”.
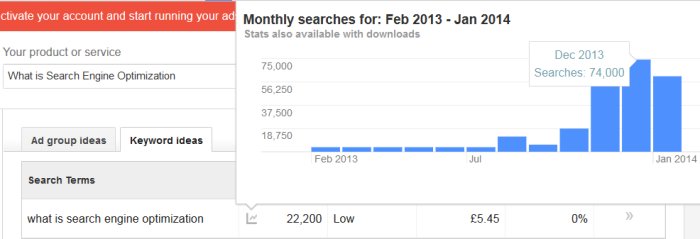
According to the AdWords keyword research tool there are around 27,000 searches a month for What is SEO and 22,000 for What is Search Engine Optimization. These won’t all be type in searches, some of the searches are due to the “Searches related to …” suggestions.
Those numbers do not show the true picture, as you can see from the screenshot below the What is Search Engine Optimization search wasn’t popular until November 2013, as you can see for February 2013 to October 2013 there was barely any searches. whilst later in the year the search numbers shot up to 74,000 a month!
What you are seeing here is Google adding a new “Searches related to …” suggestion for SEO searches. Guess when the Google Hummingbird algorithm was rolled out? End of September 2013.
I’m targeting this article at What is SEO and derivative search phrases. I could stuff this page with the phrase “What is SEO” (and I have obviously included the term) and 5+ years ago that would have been more than enough with lots of backlinks using that exact phrase as the anchor text to rank well.
Google is looking for this type of unnatural SEO or more precisely looking for web pages that are using more natural language to show it’s users. You can not optimize a web page for a single phrase any more, endlessly repeating the one phrase to a specific keyword density. In 2014 you have to cover as many semantic alternatives/derivatives of the phrases as possible as that’s what real people are searching for and Google is guiding them to.
What is Semantic SEO?
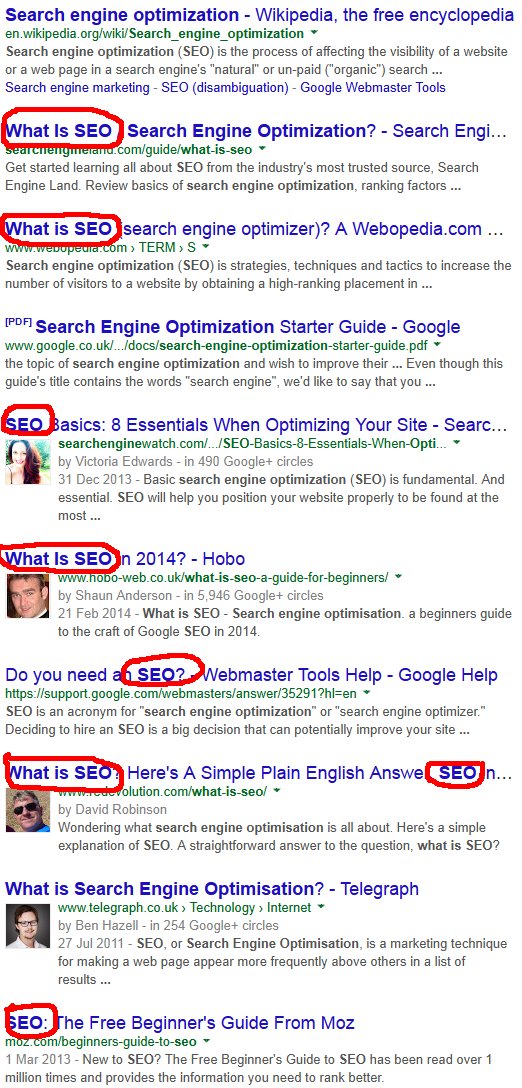
Go do a Google search for What is Search Engine Optimization and note how only one of the results include the exact search match within the title tag, but four of the results include the exact phrase What is SEO and it’s bolded indicating Google considers What is SEO and What is Search Engine Optimization as semantically the same: either the same meaning or very closely related.
This is the new SEM 2014, cover your search phrase by using your targeted keyphrases semantic versions as well, basically use phrases that have the same meaning.
SEO = Search Engine Optimization (it’s an acronym, but the same concept applies)
Market = Marketing = Markets
Search = Searching = Searched
Google can to some degree pull the meaning of text from a webpage, not just the basic keyphrases, so we have to provide Google with easy to understand content.
David Law


Social Networks and SEM - The Complete Syndication Revelation
Figured I would drop a link here. Please feel free to remove it if you object. This pdf article gives a very interesting perspective on Social Networks and how to make them work with SEM. But even more interesting is how this article promotes WordPress as THE system to use for the best SEM results. (I am not an affiliate of Charles or anything – just get his emails as he has some very good information that is usually ahead of the curve.)
Aside from the SEM info in this article, I figure that the info here is a third party verification of why WordPress is a great system to use. – Even better if used with the Talian Google Adsense and SEO WordPress template!
Social Networks and SEM - The Complete Syndication Revelation
Learn Internet Marketing for Free
Hey Clayton,
Not really the place to discuss this, but I read some of the The-Complete-Syndication-Revelation.pdf file and wasn’t particularly impressed. It’s the usual waffle with little meat of how to actually achieve anything useful, I didn’t look in full detail, but they usually then go to some sort of paid course/membership to make your wallet a little lighter to gain information that’s freely available anyway.
The ones I find funny are advising how to make money by selling something and their proof is the sales from the course you are buying! So if I buy your course I prove your course works because I bought it, I don’t think so!
I’ve never paid for a course to learn anything about Internet marketing, not a member of any paid membership deals etc… in fact my only costs are domain registration and server costs and yet I know the vast majority of the sort of stuff talked about in these types of courses (I choose not to do a lot of it, limited time). There’s loads of places to learn from for free like DigitalPoint forum.
David Law
Learn Internet Marketing for Free
SEO vs Accessible Web Design
This used to be an article (wrote in 2006), but didn’t focus on an SEO subject particularly well, so moved it to a comment (hate to delete content, even if it isn’t gaining traffic).
There was discussion in the NG alt.internet.search-engines “comparing seo techniques [was: To hyphen or not to hyphen]” partially based on a web page titled “How to get IE6 to apply image border styles on hover (mouseover)?”
The owner of the site (which I think is no longer online) in question Locus Optimus (Els) is a web designer who focuses on accessibility based web design, a growing niche market due to recent web site accessibility legislation.
Free SEO Analysis
If she came to me as an SEO client with the primary goal of accessibility since that’s her niche market in web design and compromising accessibility would damage the sites credibility (I have SEO clients with similar needs, and you are a pain in the neck :-)) my search engine optimization advice would be as follows.
Consider putting the logo area to the bottom of the code, this will push your pages content to the top of the code giving a possible SEO boost and making it more accessible to blind visitors using audio browsers (less need for the hidden “Skip to content” link by doing this as well). This allows you to add a relevant alt attribute to your logo image without affecting accessibility (very few visually impaired readers will get that far in the code), it really should at least say “Accessible Web Design Home Page” for your site (if it was just for SEO reasons then “Accessible Web Design” since that’s the home pages main SERP).
Oops, should have looked at the code for the page first, you’ve made two “mistakes” with the logo code.
First problem is it’s surrounded by a H1 header.
Second you’ve added a blank title attribute.
That’s a complete waste of a H1 header from an SEO perspective and unless you are using CSS to show an alternative to the image for text based browsers there’s no reason to have it there.
Title attributes are shown as tool tips when hovering over an image in preference to the alt attribute when using Internet Explorer, so viewers see nothing when they mouseover that image. You shouldn’t use the title attribute and alt attribute together for this reason. Since the title attribute is currently ignored by Google my advice is use only the alt attribute on images and the title attribute (if you must use it) on text links and similar items where the title attribute is displayed (but don’t expect an SEO boost in Google by using the title attribute, it’s ignored).
Speaking of headers the hidden H2 Navigation header should be replaced with another tag (span would be my choice) so as not to tell search engines the word Navigation is important. You should also change the H2 header with “How to get IE6 to apply image border styles on hover (mouseover)?” to a H1 header since that’s the title of the main content of this page (it should be considered most important hence H1).
There’s no menu on this page and only a small menu on other pages. There’s some benefits to having a menu, (again you can put it at the bottom of the code for SEO and accessibility reasons) and benefits to not having a menu. Really depends on the site in question.
Main benefits are your main pages receive a link from every page of the site, which tells the search engines which pages of your site are the most important (say it with links not flowers :-)) and it makes navigation of a large site much easier.
Biggest negative is every page has the content within the menu and this will ‘water down’ the relevance of most pages. This depends exactly what is within the menu of course, a site that is highly targeted to a small set of similar SERPs the menus anchor text is likely to use keywords that will help most pages of the site so you get an SEO advantage using a menu with relevant anchor text. Conversely a large site with no real focus or theme the anchor text is likely to not help many pages of the site and so could hinder your SEO efforts.
An alternative to a menu is a set of contextual links from either within the content or above/below it. These should be the most relevant pages to this pages theme. The link with anchor text “solution: get IE6 to apply image border styles on hover.” is a relevant contextual link, there are other pages that are highly relevant to this page that should be linked from here as well.
The set of number links at the top of the content should be deleted, they aren’t good from an SEO or accessibility stand point (I was surprised to see them?). For a partially sighted visitor it’s going to be a pain hovering over a set of small numbers to see a difficult to read title attribute (harder than carefully worded anchor text). Add your contextual links at the bottom and no need for these links.
I’m also surprised at the colours used for a site targeting the accessibility web site design market, those number links are very hard to distinguish as links because of the anchor text colours. Also red text on a white background, wouldn’t be my first choice, (I personally like the design, but I think it could put some potential clients off) it has to be black text on a white background for the most contrast (play it safe). I would be interested to here if there’s some research that these colours are easy to read relatively speaking?
The poppy image really should have alt text for both SEO and accessibility reasons. It’s not part of the templates structure (spacer image), those should have a blank or * alt attribute. It is part of the main content and deserves an alternative description. What exactly is a blind visitor to the page using an audio browser to take from this?
I appreciate the text goes on to explain the problem (I quoted well to make my point above :-)), but I can see confusion caused by the lack of an alt attribute here.
Wouldn’t poppy.jpg better be represented by a description like “When viewed in IE5 or IE6 the border of this image remains unchanged” (I’m sure there’s a better description than this in the sites owner).
Then we come to the title element (saved the best until last).
The current title element is-
This part of a web page is probably the most important when it comes to gaining a pages main SERP. For this reason it is advisable to include only the main SERP IF it makes sense to searches viewing the title as part of a Search Engines Results Page (SERP.) A search on Google for “CSS: how to apply mouseover styles on images in IE6” (not what I’d say is the main SERP, but I knew I’d find the page this way :-)) shows this-
As you can see the title is cut off mid stream, but doesn’t hinder with understanding what the page is about, the structure (page title, Company name, copyright notice) won’t cause problems with click thrus.
The next question is does it target the main SERP(s) for this page in the best way?
For this you need to determine what the main SERPs are. Based on the pages file name ie-image-border-styles-on-hover it suggests the author believes these words are important-
IE Image Border Styles on Hover
The content suggests these words are important-
CSS IE6 image border styles on hover mouseover
Based on this information and a little research I’d advise the following title element-
CSS Solution to IE6 Image Border Hover Styles Bug
It’s a little longer than I’d like, but accessibility is a priority for this site. The above title element doesn’t take branding into account, but I very much doubt the owner of the site can afford a strong branding campaign and with a PR4 home page she really can’t afford to add the sites name and copyright notice to the title (never waste a title element).
Other general advice would be link to this page from other related pages on the site and other sites under the owners control with relevant anchor text. If you can put those links within content (contextual linking) that’s even better than having a list of links at the top/bottom of the content.
David Law
SEO vs Accessible Web Design