It’s September 2016 as I update this old SEO article, just 3 more months before 2017. Simple concept, let’s speculate where SEO will be in 2017?
I’ll be honest, I’m not sure where Google will go SEO wise in 2017. Obviously there will be more of the same improved. So BrainRank/Hummingbird will get better, they’ll probably take more mobile responsive design into account. Since I first wrote this the Google PageSpeed Insights Tools test has got harsher, really hard to stay in the green. I even got some warnings about AdSense ads being too big on smaller device sizes and had to modify Stallion Responsive mobile CSS rules to load smaller ads on smaller devices.
I look forward to Google SEO 2017.
Google SEO 2016
One of the big things with Google SEO this year is it’s new BrainRank algorythm, announced in late 2015 by Google’s Greg Corrado. BrainRank is now a major part of the Google algorythm.
“RankBrain is one of the hundreds of signals that go into an algorithm that determines what results appear on a Google search page and where they are ranked”. “In the few months it has been deployed, RankBrain has become the third-most important signal contributing to the result of a search query” : Greg Corrado.
BrainRank is an extension of HummindBird, it’s an advanced machine learning AI (not a true AI). Basically Google is getting better at understanding what a searcher is looking for. Going beyond the mere keywords, but their meaning. In simple terms if you search for phrases, Google is much better at knowing what you want.
If someone asked you “Where Can I Buy a Used German Car?” you wouldn’t show them webpages about random Cars or Cans or Germans, you might search for auctions that sell VolksWagon (VW is a German car brand) and suggest a VW car. Google’s BrainRank isn’t this good (not true AI), but it might suggest auction sites that do sell German cars even though you didn’t ask for an auction website (I didn’t check the SERP).
Google SEO 2015 History
Before we can speculate about 2015 SEO, let’s take a look at the history of SEO up to 2015.
When I first started to learn about search engine optimization in the early years of the new millennium, Google optimization was DUMB, I mean really, really simple in the head, village idiot stupid :-)
A decade plus later, Google in 2014 is still a bit on the dumb side, but they’ve added some valuable coping mechanisms for their simplicity.
Before I got into search engine optimization, SEO in the 90s was keyword stuff your title tag and meta keywords tag. The time of Disney Porn was born, porn sites would add the most high traffic keywords to their meta keywords tag for high traffic and for a time it worked in the popular search engines of the day.
Now 2014 Google ignores the keywords meta tag completely and we can assume that won’t change for search engine optimization 2015.
After 2000 SEO used be about stuff your content with keyword rich text and add as many backlinks (PageRank was really important) using keyword rich anchor text (really important) as possible.
You could even go as far as SEO SPAM just one short phrase per webpage, if you wanted a SERP like SEO 2015 you would create a single webpage targeting that one phrase, fill the content with that exact phrase “SEO 2015” (no need for any synonyms**) and create as many backlinks with anchor text “SEO 2015” as you could beg, steal and borrow.
I was really good at this type of SEO, it was really easy to obtain SERPs.
**Google didn’t consider synonyms like SEO and Search Engine Optimization as related, just two separate SERPs, in 2014 synonyms are important to SEO, I expect in 2015 synonyms will be equally or more important, so for this article I ideally should mention search engine optimization 2015 :-)
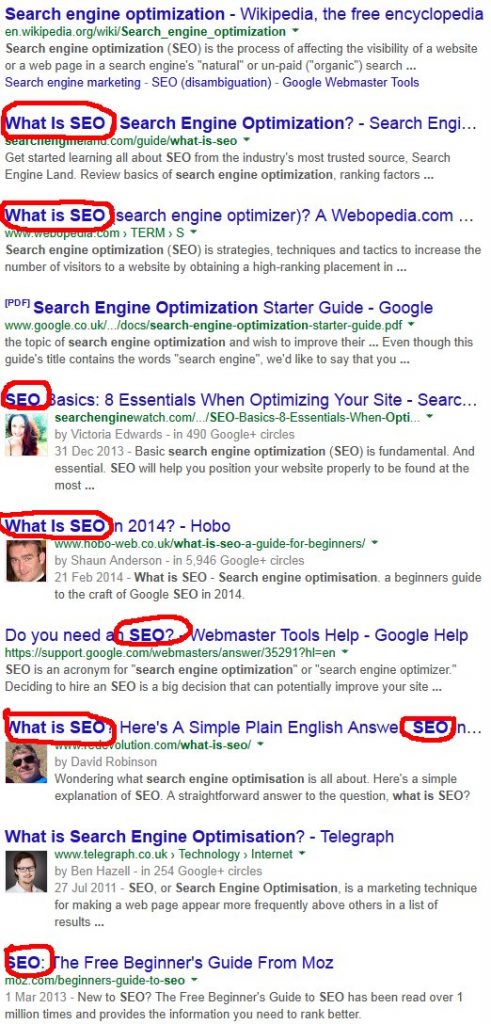
The screenshot below shows synonyms in action. A Google search for “What is Search Engine Optimization” finds pages optimized for “What is SEO?”.
Google knows two users searching for “What is Search Engine Optimization” and “What is SEO” are looking for the same content.
Google Search Engine Optimization Difficulty
By 2010 Google SEO had really turned a corner, Google was making it harder and harder to compete for even semi-competitive SERPs. PageRank and the anchor text of links though still very important, because Google was adding more and more SEO metrics (in 2014 Google says they use over 200 ranking factors) the value of any one SEO metric is reduced.
To understand this, let’s say in 2000 Google had 50 ranking factors, if in 2010 it was 100 SEO metrics you can see the 50 factors used in 2000 can’t all have the same SEO value as before (most will pass less SEO value). Google uses over 200 metrics today, for 2015 it’s likely to increase further with Google taking pagespeed factors and usability into account, a new SEO metric was announced just last month an https/SSL update giving a small boost to secure websites: this is a new Google usability metric.
Because Google has added a new ranking factor the current factors must as a whole must have less SEO value. If yesterday there were 200 factors and today it’s 201, the new factors value must be taken from the other 200 factors.
What to take away from this is as Google adds new SEO metrics the old ones that aren’t dropped (for example meta keywords are no longer a Google ranking factor) will most likely have less of an impact.
Google recently stopped showing Google+ author profile images next to SERPs, screenshot below shows a Google search from early 2014, the same search no longer shows my image.
I don’t know if in early 2014 Google gave a ranking boost for associating articles to a Google+ author (we associated sites with Google+ for the image, hoping for a higher click through rate from Google). I also don’t know if in late 2014 Google removed a ranking boost for Google+ author association. Google makes regular algorithm changes, it will add new factors, remove old factors and change the value of ranking factors over the medium to long term.
This does NOT mean what was important 10 years ago (PageRank, anchor text, title tags etc…) are no longer relevant at all, just means you still have to work on PageRank, anchor text, title tags etc… but the SEO impact of those older ranking factors won’t have the same impact as they had in previous years.
Used to be possible to rank high in Google just by adding loads of high PR backlinks from any site with the links anchor text matching the SERP you wanted: basically 10 years ago if I wanted this page to rank high for a SERP like “SEO 2014”, it could be achieved with three main SEO factors, title tag = “SEO 2014”, use “SEO 2014” a lot on the body text, add LOTS of backlinks with anchor text “SEO 2014”, it was the backlinks with exact match anchor text which had the greatest SEO impact.
This concept still works, but you have to be far more subtle, now you want the anchor text of the backlinks to be varied, you have to avoid backlinks from any source, think twice about sitewide backlinks and be more careful on over optimizing (keyword stuffing) the body text. Even then because there’s so many more SEO factors, for competitive SERPs the above isn’t enough, the above only covers a handful of the 200+ SEO factors.
I’m afraid in 2014 it means more work for webmasters and that’s likely to increase further in 2015 with the new Google ranking factors coming online.
2015 SEO : Performance and Usability
In 2014 we have seen Google via their Google PageSpeed Insights Tool indicate website usability and performance will be important in 2015.
When talking about Google SEO 2015 it’s speculation, we won’t know for sure until Google rolls out new algorithm updates and SEO experts like yours truly test their impact. This is NOT a Google released an algorithm update called Google Pigeon and within days we (SEO experts) know it’s full impact, it takes months of analysis and SEO testing to gain insights into what Google has done and by that time Google has released the Google Duck-Billed Platypus update (now that would be a cool name for a Google algorithm :-)) making it even harder to determine what a previous change resulted in.
Basically what Google changes in 2015 will probably be known for the most part in 2016 by which time it will have changed again!
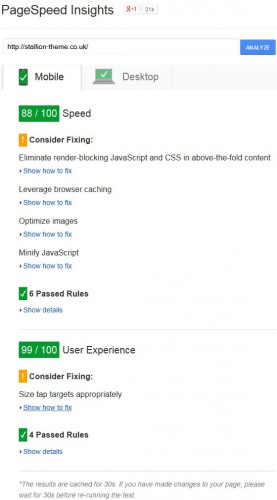
Run your site through the Google PageSpeed Insights Tool
Google PageSpeed Insights Tool
Are your results all in the green like my site? The above results are for my site.
The Future of SEO 2015
If I’m right that Google will be shifting more ranking value to performance SEO and usability in 2015 try to fix your website Google PageSpeed Insights issues now. You won’t be able to fix them all, but there’s a lot that can be improved on almost any website from dumping features that are heavy on resources to simply optimizing the size of images. Your goal should be aiming for green, if you check other websites in your niche right now you will find most are in the amber or red, get your website in the green and when (if: I could be wrong, I don’t know the future) Google takes these performance and usability more into account in 2015 you will be ahead of your competition on these newer SEO factors.
My website runs on the WordPress SEO Package Stallion Responsive (I’m the developer), which with the addition of a couple of WordPress plugins I’m able to push my Google PageSpeed Insights results into the green for mobile usability, mobile pagespeed and desktop pagespeed.
I’m ready for Google 2015, are you?
David Law


SEO in 2015
Hey Dave – just read your post for SEO 2015 and I agree with you. SEO in 2015 will be more inclined towards website performance and usability. I’ve been in SEO since last 10 years and have seen the transformation from the very beginning, right from keywords enriched spammy text to long tail keys and content.
The year 2015 will be totally for users, user experience, website responsiveness and mobile experience.
SEO in 2015
SEO Ranking Factors and Rank Correlations 2014
SearchMetrics just released their SEO Ranking Factors and Rank Correlations 2014 study data http://www.searchmetrics.com/en/knowledge-base/ranking-factors/.
It’s 80+ pages of info/SEO data I’ve not gone through completely yet (always makes for an interesting read), so not writing this comment to discuss what were/are the most important Google SEO ranking factors for 2014 and probably important in 2015, but how these sorts of SEO data results are generally misinterpreted by non scientists.
I don’t blame SearchMetrics for the SEO research, it’s generally very good SEO research and they warn users this is correlation NOT causation, though I find this distinction is lost on most SEO’s and webmasters.
SEO Correlation vs SEO Causation
Every morning a cockerel crows on the farm and the Sunrises.
We all know a cockerel crowing does not cause the Sun to rise, this is correlation not causation, yet some in the past will have believed the cockerel crowing caused the Sunrise.
Without scientific study you might assume the Sun rising per se would CAUSE the cockerel to crow (this would be causation, the light from the Sun rising causes the action), but an article in Cell (science magazine) indicates cockerels have an internal biological clock and will crow without seeing the dawn (they still crow in a dark room). So even the crow of the cockerel isn’t caused by the Sun rise per se, there’s clearly a link: the biological clock is in sync with the Sun rise, but from the info we have we can’t be sure it’s actually the Sunrise that’s the direct cause.
Never assume because A occurs when B is present, B causes A.
This is the basic scientific process and an essential tool when analysing SEO data.
I was looking through the WordPress support forums recently and read a support question how to organise their title tag and meta tags in this format code wise:
Title TagMeta Description Tag
Meta Keywords Tag
The person who asked the question had researched a SERP they wanted for their website and found the top websites for that SERP all had the above meta tags format.
This is again SEO correlation not SEO causation. Google ignores the meta keywords tag completely and doesn’t use the meta description tag as a ranking factor and though where some content is located in the code is a ranking factor, the above is not a ranking factor.
Humans have evolved to search for patterns, we are amazing at finding real patterns, but it leaves us open to finding patterns where none exist. Examples of finding patterns where none exists include:
Lucky Trinkets : Rabbits foot, lucky horse shoe, lucky item of clothing.
Religion : We pray and sometimes good stuff happens.
Astrology : Yep, the alignment of the stars and planets as seen from Earth control our destiny!
Faith Healing : Placebo effect/coincidence.
At my core I’m a scientist and if a result can’t be repeated under scientific conditions it’s not been proved and shouldn’t be be relied upon as a fact.
Looking through the SEO Ranking Factors and Rank Correlations 2014 data there are so many data points that can easily be explained as SEO correlation not SEO causation.
Social media for example, over recent years many in the SEO industry have moved to believe social media metrics are a huge SEO ranking factor. Facebook likes, Google+ shares, Twitter mentions etc… and a whole industry has developed selling Facebook likes etc…
This is not to say social media metrics are not ranking factors, but the way webmasters interpret the data isn’t scientific and can not be relied upon. Google might completely ignore Facebook likes, Twitter mentions… the SEO data available doesn’t indicate either way.
The SEO correlation is when looking at webpages that rank high in Google there’s a tendency for those pages also to have a strong social media footprint (lots of Twitter mentions, Google+ shares, Facebook likes…
The SEO question, is the strong social media footprint a cause of high Google rankings or an artifact of high Google rankings?
It’s not easy to scientifically test this.
How do you setup an SEO test where you generate webpages with a strong social media footprint without also generating other known SEO ranking signals like backlinks?
Let’s say you have a network of social media users willing to like and share your content for an SEO test, once they start liking and sharing the content their followers etc… will see the content and start liking and sharing as well and some will add backlinks from blogs etc… and we know backlinks are very important to Google rankings: are SEO ranking increases due to the social media footprint or the new backlinks and additional visitors or other factors?
It’s practically impossible to test possible social media ranking factors independently of other factors. Being popular on social media sites will increase other important SEO ranking factors.
We have two possible conclusions.
A strong social media footprint results in better Google rankings.
or
Better Google rankings results in a strong social media footprint.
With the former social media activity is a (major) ranking factor.
With the latter social media activity isn’t a (major) ranking factor, it’s an artifact of higher traffic.
Current SEO data doesn’t provide a clear answer.
All we really know is popular websites tend to have a strong social media footprint, but that’s not universally true. This website has a weak social media footprint and for a website that’s under one year old is ranking high in Google. This doesn’t prove social media metrics per se aren’t important at all to Google, suggests if social media is a ranking factor, other SEO factors are as or more important. I wouldn’t conclude from this one data set that social media factors aren’t important.
You can see the difficulty in determining what is and isn’t important SEO wise. For this reason my SEO approach tends to be remove as many factors I know causes SEO damage (like rel=”nofollow” links) and work on factors that I either know for sure have SEO value (I know backlinks are important) and work on factors that won’t cause harm and might help.
There’s indications Google in 2015 will consider usability as a more important SEO factor, making a website better for users doesn’t damage a site, therefore it’s a good factor to work on even if Google doesn’t consider it that important.
On the other hand I know Google completely ignores the meta keywords tag, so spending time optimizing the meta keywords tags is a complete waste of time: adds nothing for users, adds nothing for Google and since adding a meta tag that doesn’t achieve anything is a waste of resources it could be argued is SEO damaging.
David
SEO Ranking Factors and Rank Correlations 2014
SEO in 2015
Nice prediction. I hope the Performance and Usability factors will come true so that there will be some control over complexity in web technologies like UI design and functionalities. Thanks for giving light on “synonyms in action” section, still we cannot say other ranking factors are not there.
Only Scored 67/100 on PageSpeed Insights
Hi Dave,
my www.aid-renegade.com site brings up a few problems with render blocking and unspecified browser caching for some images. Is there a simple sample of caching control code I can add to or is there a stallion setting I should be using? I’m currently using responsive with default ‘straight out the box’ settings.
Thanks (from a non coder)
Only Scored 67/100 on PageSpeed Insights
W3 Total Cache Performance SEO
I see you’ve already gone the route of W3 Total Cache plugin for performance SEO (recommended plugin to use with Stallion Responsive), I guess after posting the comment as your mobile score is a respectable 84/100.
Respectable because you mostly have PageSpeed Insights Issues related to resources not under your direct control. Nothing you can do about Amazon, Facebook and other off site resources that have PageSpeed Insight issues.
Use AdSense Responsive ad code the responsive code is loaded asynchronously (which is better).
You are left with a few issues you can improve: currently no solution for the “Eliminate render-blocking JavaScript and CSS in above-the-fold content” related to the main CSS file. Only way to get rid of this is run only inline CSS, not a good solution (worse than the issue).
You have 5 Leverage browser caching issues on your site. The JS file and CSS file and the images don’t have an expiry date set.
I’ve had this issue with some sites (not all). I used to think W3 Total Cache could set all expiry dates for all resources, but I think it doesn’t work with all server setups.
These are the settings I use, they might not be best for you, different servers, basically everything listed below can be achieved by your server without using W3 Total Cache, so with some servers part of it is already done via your server settings (which are harder to manage than W3 Total Cache).
Check W3 Total Cache “Performance” >> “General Settings” : “Browser Cache: Enabled”.
W3 Total Cache “Performance” >> “Browser Cache”
I tick all options except
“Prevent caching of objects after settings change” (this option is listed 3 times, don’t tick any of them)
“Do not process 404 errors for static objects with WordPress”
Under
“General”, “CSS & JS” and “Media & Other Files”
I set:
"Expires header lifetime:" >> "31536000" "Cache Control policy:" >> "cache with max-age ("public, max-age=EXPIRES_SECONDS")"Under “HTML & XML”
"Expires header lifetime:" >> "43200" (still testing the best value) "Cache Control policy:" >> "cache with max-age ("public, max-age=EXPIRES_SECONDS")"This should fix the css file, js file and image Leverage browser caching issue if the W3 total Cache options work with your server.
Remember when testing with the Google PageSpeed Issues Tool it caches the results, so if you check a page in the PageSpeed Insights tool, fix the issues via W3 total Cache or a via server settings and check again you might still get the same issue even though it’s fixed (you are seeing a cached result).
Easiest way to deal with this is check another webpage on your site, go to a post or a category and run the PageSpeed test on a fresh page.
Have a feeling the rest of this will loose you, so let’s hope W3 Total Cache options above works on your site.
If W3 Total Cache can’t set the expire headers it’s a server setting that because of all the different server configurations is hard to explain.
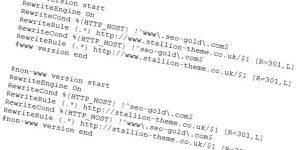
I used these options added to the main httpd.conf config file for the domains (virtualhosts) I had problems with
For example I didn’t need the above for this domain, but did need it for a sub-domain of this domain. Couldn’t get a CDN sub-domain to use the W3 Total Cache expire options (don’t know why, gave up and used the above), to get it working added the above rules to the sub-domains virtualhost.
You’d need to contact your host regarding the above IF you need to go this route.
David
W3 Total Cache Performance SEO